Radiofrequency ablation, sometimes referred to as RFA, is a minimally invasive treatment for cancer. It is an image-guided technique that heats and destroys cancer cells. Under the guidance of image, RFA, a physical method to inactive and kill the tumor, is performed with minima.
What is RFA (Radiofrequency Ablation)?
Radiofrequency ablation, sometimes referred to as RFA, is a minimally invasive treatment for cancer. It is an image-guided technique that heats and destroys cancer cells. Under the guidance of image, RFA, a physical method to inactive and kill the tumor, is performed with minimally invasive paracentesis to introduce the heat generator into the tumor. Ablation is targeting and can affect the tumor strongly while no side effect happens to normal tissues around. The result of RFA is same as invasive surgery, so it is a special knife without operation—Ablation knife.
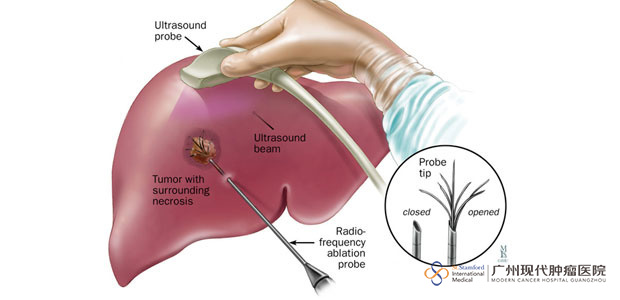
How does the RFA work?
With needle of radiofrequency ablation and multipoint temperature monitoring system, RFA’s highest temperature could reach 125 degrees Celsius. The safety is assured with the real-time monitoring over the targeted region during operation. Operation is performed under the guidance by medical image equipment like DSA, CT or type-B ultrasonic, etc. Then an electric probe, which has 10 pins on the leading end of electric probe, is inserted into the tumor via skin puncture, 10 small pins would stretch to grasp the tumor firmly when it is started. With the help of high-frequency current, high speed ionic vibration and friction would happen to the tissue around the pins to generate heat. When the temperature reaches 80-100 degrees Celsius, tumor would be heated that coagulation necrosis occur on the tumor and part of tumor cells would be killed.
Procedures for RFA
Image-guided, minimally invasive procedures such as radiofrequency ablation are most often performed by a specially trained interventional radiologist in an interventional radiology suite or occasionally in the operating room.
You will be positioned on the examining table.You may be connected to monitors that track your heart rate, blood pressure and pulse during the procedure.A nurse or technologist will insert an intravenous line into a vein in your hand or arm so that sedation medication can be given intravenously.The area where the electrodes are to be inserted will be sterilized and covered with a surgical drape.Your physician will numb the area with a local anesthetic if the procedure is to be done while you are awake.
Using imaging-guidance, your physician will insert the needle electrode through the skin and advance it to the site of the tumor.Once the needle electrode is in place, radiofrequency energy is applied. For a large tumor, it may be necessary to do multiple ablations by repositioning the needle electrode into different parts of the tumor to ensure no tumor tissue is left behind.At the end of the procedure, the needle electrode will be removed and pressure will be applied to stop any bleeding and the opening in the skin is covered with a dressing. No sutures are needed.
Your intravenous line will be removed.Each radiofrequency ablation takes about 10 to 30 minutes, with additional time required if multiple ablations are performed. The entire procedure is usually completed within one to three hours.
How should I prepare?
You should report to your doctor all medications that you are taking, including herbal supplements, and if you have any allergies, especially tolocal anesthetic medications, general anesthesia or to contrast materials containing iodine (sometimes referred to as "dye" or "x-ray dye"). Your physician may advise you to stop taking aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or blood thinners for a specified period of time before your procedure.
Prior to your procedure, your blood may be tested to determine how well your kidneys are functioning and whether your blood clots normally.
Women should always inform their physician and x-ray technologist if there is any possibility that they are pregnant. Many imaging tests are not performed during pregnancy so as not to expose the fetus to radiation. If an x-ray is necessary, precautions will be taken to minimize radiation exposure to the baby. See the Safety page for more information about pregnancy and x-rays.
You will likely be instructed not to eat or drink anything after midnight before your procedure. Your doctor will tell you which medications you may take in the morning.
You should plan to have a relative or friend drive you home after your procedure.
You may be asked to wear a gown during the procedure.
What are Clinical Application of the Radiofrequency ablation?
Radiofrequency ablation is used to treat many types of liver cancer. The two most common types are: hepatocellular carcinoma, which is a primary liver cancer (meaning it begins in the liver). colon cancer that metastasizes or spreads from the colon to the liver.
In general, radiofrequency ablation is most effective treating primary tumors, which are smaller than dia.5cm and the quantity is less than 3, tumors that are less than one and a half inches in diameter
It may be used in addition to chemotherapy or radiation therapy or as an alternative to surgical treatment.Radiofrequency ablation is a viable and effective treatment option if:
You are not a good candidate for surgery because your tumor is difficult to reach.
You have other medical conditions that make surgery especially risky.
You would not have enough liver tissue left for the organ to function adequately following the surgical removal of a tumor.
You have liver tumors that have not responded to chemotherapy or that have recurred after being removed surgically.
You have several small liver tumors that are too spread out to be removed surgically.
08.6568.4479